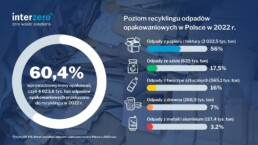
According to a report published by the Institute of Environmental Protection - National Research Institute, the recycling rate of packaging waste in 2022 was 60.4%. More than half of the recycled packaging waste (56%) was paper and cardboard waste. The highest recycling levels of either 89.1% or 83.9%, depending on the methodology used, were also recorded for this fraction.
Only and as much as 60.4% recycling of packaging waste
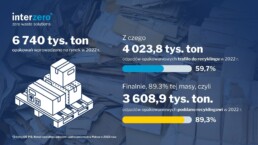
According to calculations by IOŚ-PIB experts, products packed in 6,740 thousand tonnes of packaging were put on the market in 2022. Data from 532 installations were taken into account, with a total of 4 023.8 thousand tonnes of waste entering the market in 2022. More than 10% of this mass consisted of so-called non-target materials (materials that are not recycled in a given recycling process into products, materials or substances that are not waste). After adjustment, the total the weight of recycled packaging waste was 3 608.9 thousand tonnes, including:
- 2,022.5 thousand tonnes of paper and cardboard packaging waste.
- 565.1 thousand tonnes of plastic packaging waste,
- 635,000 tonnes of glass packaging waste,
- 268,900 tonnes of wood packaging waste,
- 117,400 tonnes of metal packaging waste.
According to the methodology adopted by the authors of the report, The recycling rate for total packaging waste was 60.4%, an increase of 1.4 more than the minimum provided for in the Decree of the Minister of Climate and the Environment of 19 December 2021 on the annual recycling levels of packaging waste by year until 2030.
Recycling levels: achieved according to introducers, not achieved according to EIA-PIB
Recycling rates for total packaging waste were calculated in 2 options. The first one was based on data from introducers (entities that have entrusted statutory obligations to organisations) and stand-alone (entities responsible on their own). From this data, the recycling levels of individual packaging waste for 2022 were as follows:
- metals - 93.9%,
- wood - 20.9%,
- plastics - 40.7%,
- glass - 65.3 %,
- paper and cardboard - 89.1%.
According to this option, minimum annual recycling targets for packaging waste have been achieved for all types of packagingfrom which the waste originated.
The second variant calculation presented in the report was based on the methodology of IOŚ-PIB. The recycling levels calculated in this way for almost all packaging waste (except plastics) are at a lower level:
- metals - 36.6%,
- wood - 16.7%,
- plastics - 45.8%,
- glass - 45 %,
- paper and cardboard - 83.9%.
According to calculations based on the methodology of the EIA-PIB, in 2022, the introducers did not meet the minimum recycling levels for ferrous metal and aluminium packaging waste (amounting to 55% and 51% respectively) and wood (amounting to %).
Regardless of the option, the lowest recycling rate was recorded for wood waste.
BDO register as a source of data for the EIA-PIB report
The source of the data presented in the report is the BDO register. Gap takers, i.e. producers or distributors who place plastic packaging or packaged products on the market and do not report them to a producer responsibility organisation or public authority or otherwise take financial or financial and organisational responsibility for the management of plastic packaging waste or report smaller quantities than they actually place on the market, are not included in the calculations.
The analysis prepared by the EIA-PIB takes into account waste with codes:
- 15 01 01 - paper and cardboard packaging,
- 15 01 02 - plastic packaging,
- 15 01 03 - wood packaging,
- 15 01 04 - metal packaging,
- 15 01 05 - multi-material packaging,
- 15 01 06 - mixed packaging waste,
- 15 01 07 - glass packaging.
The actual amount of packaging waste generated in Poland and recycled was calculated as follows - adding up the weights of waste recycled in Poland and recycled abroad, reducing the result by the weight of waste imported to Poland for recycling.
Source: [1]